
Saturday, November 14, 2009
The "Standard" Lecture: Are the Current Forms of Lectures Really the Most Effective?

Friday, November 13, 2009
Is College Right for Everyone?

Thursday, November 12, 2009
Competitiveness and Collegiate Athletics
Wednesday, November 11, 2009
Merit vs. Need-Based Financial Aid

Brenden Duncombe-Smith
There have always been need-based financial aid awards at most major colleges, but in the recent years this has started to become the majority of the aid awarded. In the past a large portion of the aid awarded to students was merit based. Institutions of Higher Education used these merit based scholarships to attract top students. Admitting a large number of top students increases a schools competitiveness and prestige among other schools. Some college presidents dislike the idea of merit based scholar ships but feel that they are necessary for their schools to remain competitive. Robert Massa, vice president for enrollment management at Dickinson College feels that the term "merit based" is really just a euphemism for bribery. He mainly feels this way because the whole point of merit based aid is to attract students who will most likely attend more prestigious schools by offering them a very inexpensive education. Schools that offer this merit based aid often run out money for need based aid and end up having to accept a percentage of their class need aware, meaning they cannot accept any students who cannot afford the tuition. However, institutions like Hamilton college have shifted this trend to completely eliminate any form of need based aid. Largely because thinking among higher education has changed and it is now more valuable for institutions to be able to accept anyone regardless of need. While this is still impossible for some smaller schools it seems to be a turn in the right direction, away from "bribery". In addition most schools have found that the merit based scholarships go largely unaccepted by the top students.
Tuesday, November 10, 2009
A little Incentive could go a long way.
Monday, November 9, 2009
Textbook Costs Just Keeps Rising
Vinh Nguyen
Since I made a post pertaining to textbook costs last week, I decided to make another post relating to the price inflation of textbooks. On my last post, I mentioned that the expenditures most students spend on textbooks is the largest after tuition, room and board. According to this article, some colleges believe that the publishing industry is making the costs even higher by releasing new editions and packaging books with expensive study aids such as study guides, test questions, disks, etc. What is the publishing industry's response? The $3.4-billion-a-year higher education publishing industry reasons that textbooks must be continually modernized in order to grasp the students' attentions. However, the reissuing of editions forces professors into using new books, resulting in students buying new books. A recent study that was done by California's Public Interest Research Group reveals that the average time between editions is 3.8 years even when the information has not changed since the last edition. Moreover, new edition of the textbooks that were surveyed cost 58% more than the previous edition. Believe it or not, professors sometimes play a role in increasing textbook prices without knowing. Because most professors like to order textbooks that have appealing graphs and charts to keep the students' interests, these pictures can be expensive to design. Furthermore, professors are looking for more contents for teaching, leading to the addition of learning tools such as Web site access, study guides, etc. Since these additions are sometimes mandatory, students have no other options but to spend more money on them. So next time one goes to the bookstore to buy a book, think about whether he or she should get the older version or get the new version from overseas.
Friday, November 6, 2009
Wireless Classrooms: Why Requiring Laptops may not be Worth the Risks and Distractions

Thursday, November 5, 2009
Crowdsourcing: The Student Help Desk Chapter
Everyday, students call in or email IT help desks on college campuses. Accurate and timely, the IT help desk staff members provide logical and technical answers for fixing student computer hardware and software problems. The help desk process is a great invention;however, with such a high cost to uphold, IT help desks must have an alternative. Creating a student crowdsourcing database will not only save money, but also stimulate student interaction.

College IT help desks are essential on college campuses because of the amount of students, teachers, reasearchers, and administrators. With such a high demand for technical help and support, twenty-four hour help desks charge high prices for calls and emails. For example, the help desk at Indiana University charges $11.41 for calls and $9.39 for emails. In the last year, the IT help desk accepts 150,000 questions. As more problems occur with corrupt documents and poor servers around campuses, the need for help continues to rise.
Dewitt A. Latimer, the CIO at The University of Notre Dame, is a main force behind an idea to cut costs severly--by crowdsourcing. The idea is to allow students and faculty to answer each others' questions. The benfit is a low cost and an increase in interaction with one another, but there are pitfalls. Are all answers going to be accurate? Can you trust the person sitting next to you about the virus that just ate your midterm essay?
The answer is no. In order to satisy the budget cuts, crowdsourcing is a project that must be done. If a university can keep the old helpdesk, but focus on a new interaction-based help desk, the effects are all positive.
The New Look of Music Downloads
File Sharing. Most college students are familiar with the term. Programs such as Napster, Limewire, Kazaa, and Morpheus have become synonymous with the world of illegal music downloads. In recent memory, colleges have picked up on this trend and moved to stop students from using such applications. Now, some colleges have decided to change their attitude about file sharing.
Wednesday, November 4, 2009
College Health Care

The current economic climate has forced school to cut costs everywhere, including hiring freezes. However, few people realize just how badly these budget cuts affect the student health care provided at universities. The budget cuts are being passed straight down to the students, which is drastically increasing the cost of student healthcare. It is even affecting the staffing of student health centers on many campuses. At the University of Maryland at College Park the hiring freeze has caused the school to go without a psychologist, which is arguably one of the most important positions for health care on a college campus. Jon Englund author for InsideHigherEd.com, noted that one way to prevent this was for schools to start accepting more health insurance plans that students may already have from their parents. In fact Ohio University gained so much extra revenue from billing insurance company that instead of having a deficit they are now ready to expand their facilitates. They are even planning to hire more psychologists and increase the hours of the health center. This is just one solution to the problem ever increasing costs, but it is unacceptable to allow health care costs for students to increase so much. Most students are completely unaware of the fact that health care in college may be so expensive, and as a result they are very surprised when they find out how much it will cost them to be treated some even forgoing appointments to save money. Regardless of what solution is found it is clear that one is required because it is entirely unacceptable to allow students to skip treatment to save money.
Tuesday, November 3, 2009
Are the Busy Bees the Smarter ones? A comparison between working and non-working students
Monday, November 2, 2009
Ways to Saving Money Buying Textbooks
Most people know textbooks in college can be costly. According to this article from The New York Times, most students spend from $700 to $1000 a year on textbook, making it the largest cost after tuition, room and board. As a matter of fact, a recent report found that the prices had nearly tripled from 1986 to 2004, rising an average of 6 percent a year, almost double the inflation rate. For these reasons, some students mentioned in the article tried to find ways around by sharing or borrowing books from other students or buying 2 out of 15 assigned books in order to save money. Nonetheless, there are a few ways one can save his or her money.
First, one can get a new textbook but older editions or overseas, which sometimes can be less expensive yet brand new with no highlights on every page. By doing so, one can save some money while he or she can still get a complete "package", including CDs, problem sets and sometimes even a workbook.
Second, one can buy used books from bookstores or websites such as Amazon.com, Half.com, CheapestTextbooks.com, etc. The only real disadvantage to this method is that it might take a few weeks for the books to arrive if one is ordering them via online.
Lastly, not many students know that they can actually rent textbooks for half the price of a brand new textbook from websites like TextbookRentals.com, Collegebookrenter.com, etc. Nonetheless, there are some inconveniences to this method. One can't keep the book for further studying or reviewing and he or she cannot write on the book; otherwise, he or she has to pay the full price instead and ends up paying more than a brand new book.
With the economy like today, one would want to save some money, potentially hundreds of dollars, to spend on other things. Finally for the last tip, one can buy used books online, which are half the price of the brand new books, and sell them back to the bookstore for half the price of the brand new books at the end of the semester. Thus in the end, if the books are still in good condition, one will end up not paying more than $10 total for textbooks.
Saturday, October 31, 2009
The Real Danger in College: Campus Safety in the Laboratory

Friday, October 30, 2009
How to Prevent Illegal Sharing of Academic Journals
Bo Andrews
In today's modern colleges, students must read through tons of academic journals and articles to complete many projects in a variety of classes. Sites such as Google Scholar and EBSCOhost supply many articles and websites to research necessary topics; however, not all of these websites are free.

Thursday, October 29, 2009
Campus Email Addresses: A Thing of the Past?
A recent report, published by Educase, provides new information regarding the prevalence of campus provided email addresses. The report, which draws its information from over 900 universities nation wide, states that nearly 10 percent of the institutions polled are considering phasing out campus provided email addresses. When questioned, the institutes cited the use of personal email addresses as a primary reason for this course of action. This is startling considering that in 2004, a mere two percent of institutions would consider phasing out such email addresses. While I can understand the incentive to phase out such technology, the potential fiscal assets recouped would not be worth the sacrifice. Firstly, standardizing email addresses across campus allows students to use a separate email address specifically for educational purposes. Second, the standardized naming conventions prevents teachers from having to email students personally created addresses. While this may not be such an issue for most, a few will understand that when you give your teacher your email address, "drunkman45@gmail.com" isn't exactly the most shining representation of yourself. Third, and finally, use of campus email addresses creates a sense of responsibility for students. Students will be required to check their email to remain updated on class schedules and course materials. A skill that will become imperative in their future pursuits. So my response to this move to get rid of campus email addresses; keep them, but allow students the opportunity to port the campus email address to their own personal one for a simplified experience.
Wednesday, October 28, 2009
Large Lecture Classes

Brenden Duncombe-Smith
Everyone who has ever attended a college class is painfully aware of how large some of the introductory lecture classes can be. Unfortunately, these large classes have become necessary because of the large amount of students that are required to take those introductory classes. Some believe that these large lecture classes are a perfect opportunity to get well qualified professors speaking to a large group of students. However, most people believe that the large class sizes negatively affect a student's ability to learn. The main reason for this belief is the fact that large classes make for an environment with very little interaction between students and the professor. I have seen this first hand, during large lectures I notice that a large number of students are either doing other work, on Facebook, or sleeping. The reason that the problem of large class sizes still persists is because the solutions are just too expensive for the majority of colleges to successfully implement. The USA Today notes that Nobel laureate Carl Wieman is urging for reform in the teaching style of large lectures. Most notably is the use of personal response systems to instantly poll classes to see if the students are grasping the material in real time. Wieman believes that these and other tools that help students interact with the professor are the key to increasing a student's understanding of the material. Whatever the eventual solution may be, low cost solutions like the personal response system and other technological tools promise to be a key factor in solving the problem.
Tuesday, October 27, 2009
Study Abroad: Language Doesn't Matter.
Monday, October 26, 2009
Harmful Effects of Caffeine Products
Vinh Nguyen
Many students consume coffee to help them staying awake or staying up all night to either finish their homework that is due tomorrow or cram for the upcoming test. Although students might be able to stay alert during lectures or to get through the day by consuming caffeine products like coffee, there are some deleterious effects to drinking coffee in the long run such as decrease in the amount of calcium in the body according to this article. Moreover one of the effects of consuming caffeine products is that once the caffeine wears off, the consumers will be left with no stamina, resulting in body exhaustion. According to American Dietetic Association, the amount of caffeinated drinks consumed by teenagers has triple since 1970s; nevertheless, most students do not know the side effects of using too much coffee. Even though caffeine can keep students awake, studies have shown that caffeine can disrupt short-term memory, decreases productivity, and obstructs the ability to learn and absorb new information. Lastly, teenagers who consume caffeine regularly will have erratic sleep cycle, which leads to loss of behavioral control, negative mood, excessive aggression and impulsiveness. In closing, consuming too much caffeine can be dangerous and it is vital to remember that there is no substitute for a good night's sleep, which enhances students' alertness without harming them.
Saturday, October 24, 2009
The Cost of College on the Couch: The Rising Cost of Online Education

Thursday, October 22, 2009
Digitization in College Libraries
Library documents have been around since the scrolls at Alexandria. These documents have very simple formats: ink crafted on a canvas. Imagining elctronic files of books instead of countless shelves with books is a very hard concept to grasp. While New York University has begun to digitize its library, the concept of employing electronic readings as the main sources is necessary in order to preserve many oringinal documents.
 College Libraries host many students and groups that are studying or conducting research. Having the capability to access many sources through library computers presents a substantial benefit by creating a greater variety with less actual space. With less space needed for bookshelves, more tables and computers can fill in the open space. According to McMillan Memorial Library, digitizing college libraries can not only provide more sources, but also preserve the original documents and allow for "far superior access."
College Libraries host many students and groups that are studying or conducting research. Having the capability to access many sources through library computers presents a substantial benefit by creating a greater variety with less actual space. With less space needed for bookshelves, more tables and computers can fill in the open space. According to McMillan Memorial Library, digitizing college libraries can not only provide more sources, but also preserve the original documents and allow for "far superior access."According to The Chronicle of Higher Education, New York University is beginning to digiitze some sources its its main library. In order to provide global access for its students in Abu Dhabi, NYU has taken an influential leap into the employment of technology in higher education.
Digitizing college libraries has systemic effects. While more college libraries install digital sources, the more students will be able to use those resources through their own computers; consequently, more library tables will be open to study and work in groups. The digitization in college libraries is a win-win situation for every side.
Wednesday, October 21, 2009
College Drop-Out Rates
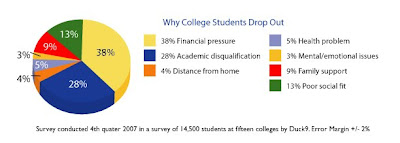
College drop-out rates are one of the most worrying problems with higher education today; however, it is one of the least understood problems. There are so many contributing factors that no one knows where to start the solution. With as few as fifty four percent of students graduating in six years it is easy to understand why a solution needs to be found. Even more disturbing the Associated Press notes that there are even larger discrepancies between drop-out rates among different races. With many schools reporting a twenty point lower graduation rate. Some blame students for not appreciating the sheer importance of a college education. Still others blame the colleges themselves for not implementing more programs to keep their students in school. Yet none of this truly matters because even if either of these were the problem they have no reasonable solution. The main solution would be for the government to offer incentives to schools based on their graduation rate. However, this would most likely to cause schools to just become even more selective, only accepting applicants who are most likely to graduate. The real victims in all of this are those students who do not graduate. They are promised an education that will get them a good job, and instead they don’t get a degree and end up with a huge debt. In most cases it would probably be better if those students hadn't even attended college because they would at least be free of student loans. The problem of the college drop-out rate is complex and hard to study a real solution won’t be able to be reached without much more study.
Tuesday, October 20, 2009
S.P.A.R.K.notes: So much Preexisting, Already thought-up, Reliable Knowledge notes

Everyone feels bad about cheating, and no one doesn't regret having damaged how they are viewed by their peers and teachers, not to mention cheating themselves out of a valuable education. Being dishonest is a reputation that is hard to overcome, so don't become a lesser person just to get a better grade.
The above paragraph is something many college professors are seeing this day. It is a reearangement or paraphrase of a talking point from a cheaters best friend: Sparknotes. (http://sparkcharts.sparknotes.com/study/distancelearning/section7.php) While ethics and honor codes on college campuses are becoming more and more strict due to the sudden surge of resources on the web, students are become lazy and looking for as many ways to get around the rules as they can. Specifically, students have become well versed in simply restating an authors thoughts, in a variety of ways, and using the "I didn't know" rule to wiggle their way out of tight spots.
Monday, October 19, 2009
How To Motivate Yourself?
Vinh Nguyen
Many students do poorly in school because they procrastinate and wait until the last minute or day to get started on their homework or project. As a matter of fact, 26 percent of Americans are procrastinators according to this article. So how can one motivate oneself to work more efficiently? There are 13 tricks or tips that can help one to increase his or her self-motivation according to this article. Some of the tricks that I personally find most useful are going back to "why", going for five, moving around, and getting a partner. Going back to "why" basically means that one needs to keep reminding him or her of why he or she is even doing the task in the first place. This strategy will help one focus on the assignments and enhance one's performance. Moreover, it will make the task more appealing. The next advice that I find helpful is going for five, meaning taking a one-minute break every five minutes of working and start increasing the working time gradually. Doing this will motivate one more because the break every five minutes mentality will make one think that the workload is less than it actually is. One thing that is important to keep in mind is that the break can't be longer than one minute; otherwise, it will ruin the purpose of this strategy. Some things one can do during the break is check his or her phone for text messages or computers for any instant messages. In addition to constantly reminding oneself of the whys and a short recess every five minutes of working, moving around such as stretching or standing up also improves ones concentration and focus since doing this will decrease the likelihood of falling asleep and getting tired while working on the assignment. Lastly, working with someone else is great to motivate oneself because that person will motivate you to work when you would normally just quit. There are 9 more tips but I will save them for another post, or readers can follow the article I hyperlinked earlier.

